What are classical, theoretical, Lagrangian, and Hamiltonian mechanics? Is it useful to know them as a mechanical engineer? - Quora
By A Mystery Man Writer
Answer (1 of 4): Classical mechanics usually refers to the mechanics of macroscopic objects i.e. anything that does not require a quantum description. It sometimes refers also to Newtonian mechanics which relies on forces to describe the systems it studies. Namely the central tennants are Newton'
Hamiltonian mechanics - Wikipedia

SOLUTION: Classical Mechanics d'alembert's Principle And The Lagrangian - Studypool

Physics 69 Hamiltonian Mechanics (1 of 18) What is Hamiltonian Mechanics?

Phy 303: Classical Mechanics (2) Chapter 3 Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Mechanics. - ppt download

classical mechanics - Is there a proof from the first principle that the Lagrangian $L = T - V$? - Physics Stack Exchange

Difference Between Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Mechanics

Classical Mechanics- Lagrange Equation / Hamilton's Variational Principle

Hamiltonian Mechanics - Wikipedia PDF, PDF, Hamiltonian Mechanics

An Alternative Derivation of The Quaternion Equations of Motion For Rigid-Body Rotational Dynamics, PDF, Lagrangian Mechanics
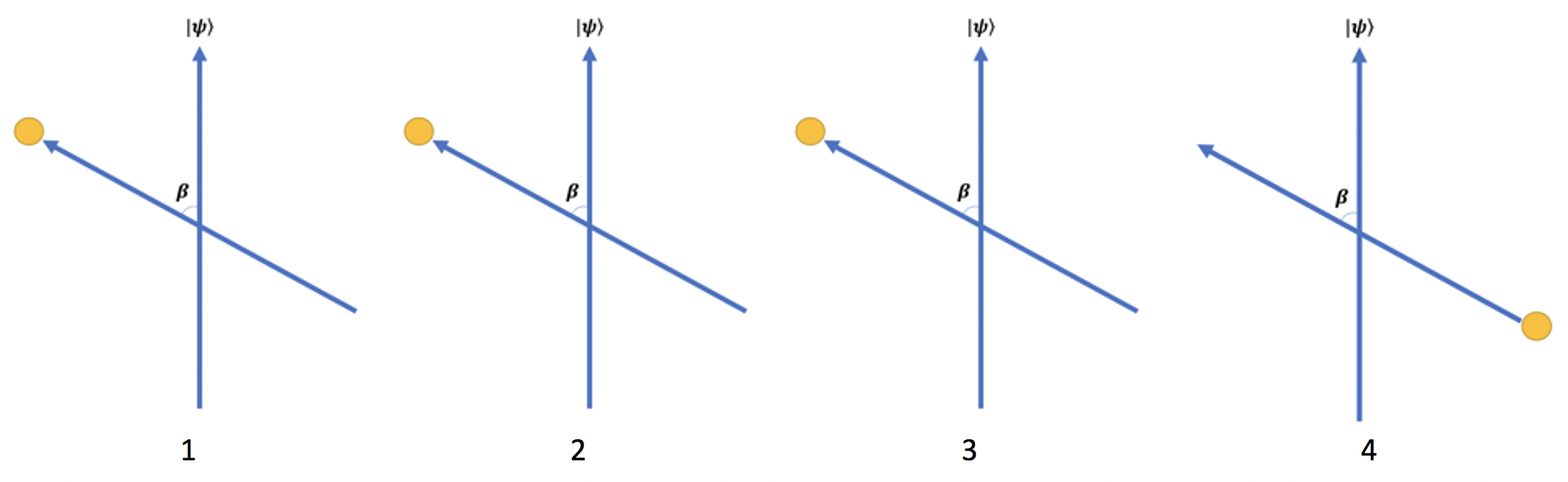
Introducing Quantum Entanglement to First-Year Students: Resolving the Trilemma
- Mechanics - Definition & Types (Classical, Quantum & Statistical)

- Classical Mechanics - University Science Books

- Modern Classical Mechanics by T.M. Helliwell

- Classical Mechanics: Buy Classical Mechanics by br. J. C. Upadhyaya at Low Price in India

- IOPP: Title Detail: Classical Mechanics: Problems with solutions by Konstantin K Likharev





